RabbitMQ
第一章 基础
1.1 基本介绍
RabbitMQ的整体架构及核心概念:
- virtual-host:虚拟主机,起到数据隔离的作用
- publisher:消息发送者
- consumer:消息消费者
- queue:队列,存储消息
- exchange:交换机,负责路由消息
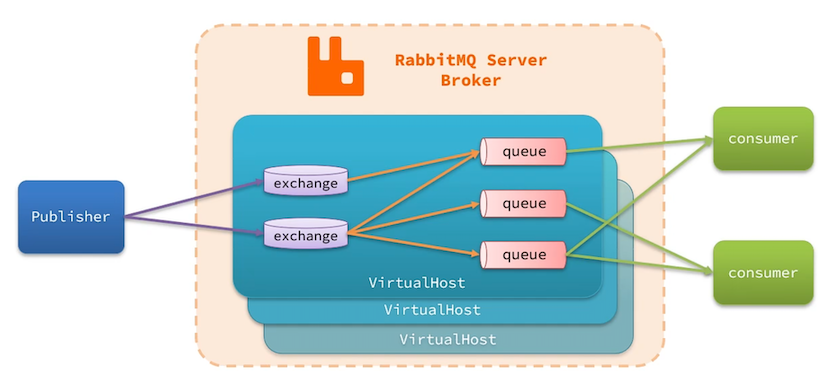
1.2 数据隔离
各个虚拟主机之间是数据隔离的
1.3 Java客户端
一、快速入门
- 控制台创建队列simple.queue
- 在publisher服务中,利用SpringAMQP直接向simple.queue发送消息
- 在consumer服务中,利用SpringAMQP编写消费者,监听simple.queue队列
SpringAMQP如何收发消息?
引入
spring-boot-starter-amqp配置rabbitmq服务端信息
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: xx.xx.xx.xx
port: 5672
virtual-host: /hmall
username: xxx
password: xxx- 利用RabbitTemplate发送消息
package com.priv.publisher;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
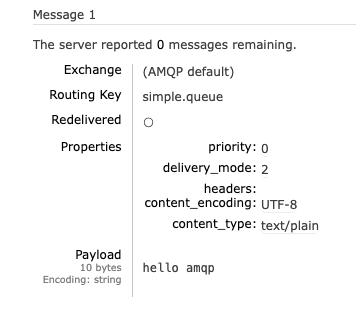
void testSendMessage2Queue() {
String queueName = "simple.queue";
String msg = "hello amqp";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, msg);
}
- 利用@RabbitListener注解声明要监听的队列,监听消息:
package com.priv.consumer.listeners;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
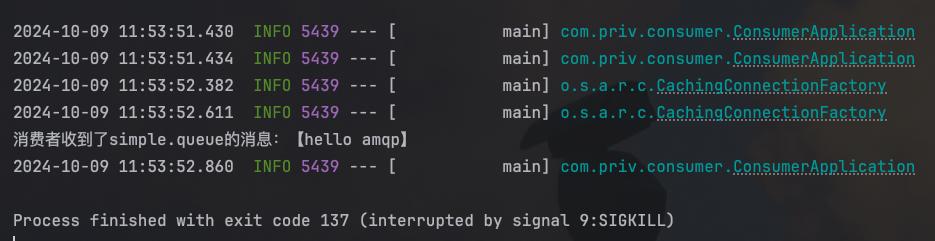
public void listenSimpleQueue(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者收到了simple.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}
二、WorkQueue
让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息
需求:
- 在RabbitMQ的控制台创建一个队列,名为work.queue
- 在publisher服务中定义测试方法,在1s内产生50条消息,发送到work.queue
- 在consumer服务中定义两个消息监听者,都监听work.queue队列
- 消费者1 每秒处理50条消息,消费者2 每秒处理5条消息
生产者
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testWorkQueue() throws InterruptedException {
String queueName = "work.queue";
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
String msg = "hello work, message_" + i;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, msg);
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}
}消费者
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者1收到了work.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
Thread.sleep(20);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("消费者2收到了work.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}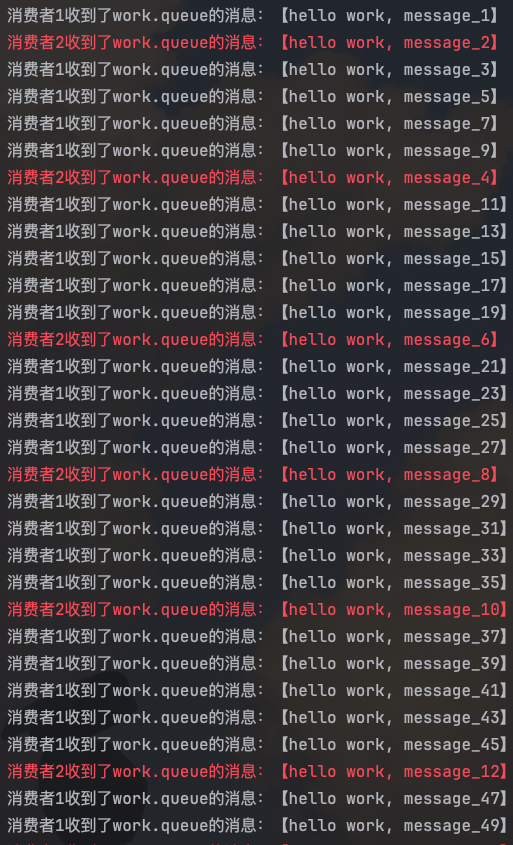

默认情况下,RabbitMQ会将消息依次轮询投递给绑定在队列上的每一个消费者。但是这并没有考虑到消费者是否已经处理完消息,可能出现消息堆积。
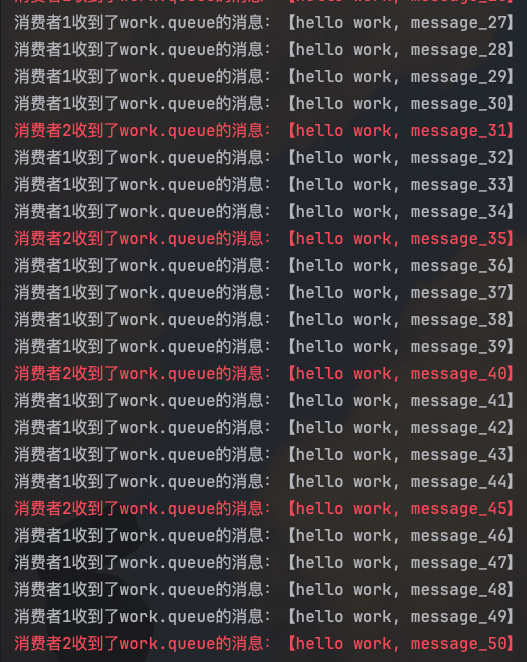
需要修改配置,设置preFetch值为1,确保同一时刻最多投递给消费者1条消息:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: xx.xx.xx.xx
port: 5672
virtual-host: /hmall
username: xxx
password: xxx
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息, 处理完成才能获取下一个消息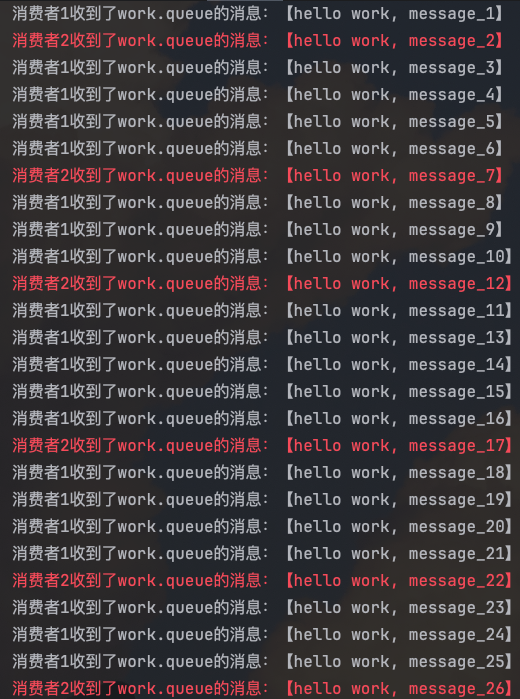
三、Fanout交换机
交换机的类型有三种:
- Fanout:广播
- Direct:定向
- Topic:话题
Fanout Exchange 会将接收到的消息广播到每一个跟其绑定的queue,所以也叫广播模式

案例:利用SpringAMQP演示Fanout Exchange
1、在控制台声明队列fanout.queue1和fanout.queue2
2、在控制台声明交换机hmall.fanout,将两个队列与其绑定
3、在consumer中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听fanout.queue1和fanout.queue2
4、在publisher中编写测试方法,向hmall.fanout发送消息
生产者
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testSendFanout() {
String exchangeName = "hmall.fanout";
String msg = "hello everyone!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "", msg);
}
}消费者
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void listenFanoutQueue1(String msg) {
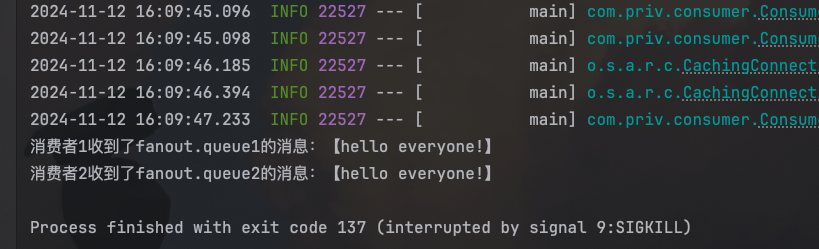
System.out.println("消费者1收到了fanout.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void listenFanoutQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2收到了fanout.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}
四、Direct交换机
Direct Exchange会将接收到的消息根据规则路由到指定的Queue,因此称为定向路由
- 每一个Queue都与Exchange设置一个BindingKey
- 发布者发送消息时,指定消息的RoutingKey
- Exchange将消息路由到BindingKey与消息RoutingKey一致的队列

案例:利用SpringAMQP演示DirectExchange的使用
1、声明队列direct.queue1和direct.queue2
2、声明交换机hmall.direct,将两个队列与其绑定
3、在consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听direct.queue1和direct.queue2
4、在publisher中编写测试方法,利用不同的RoutingKey想hmall.direct发送消息
生产者
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testSendDirect() {
String exchangeName = "hmall.direct";
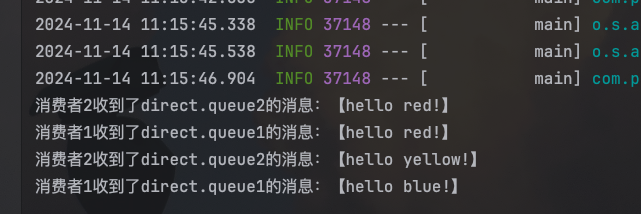
String msg1 = "hello red!";
String msg2 = "hello blue!";
String msg3 = "hello yellow!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "red", msg1);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "blue", msg2);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "yellow", msg3);
}
}消费者
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue1")
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1收到了direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue2")
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2收到了direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}
五、Topic交换机
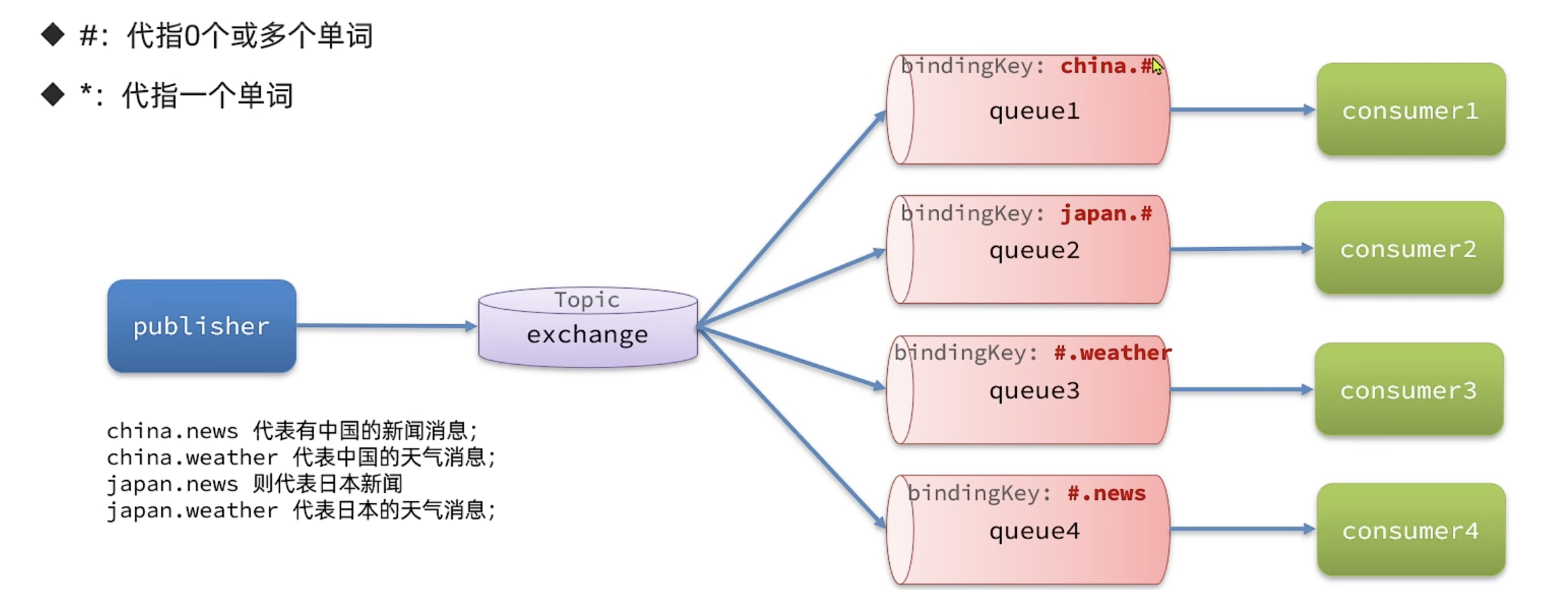
TopicExchange与DirectExchange类似,区别在于routingKey可以是多个单词的列表,并且以.分割
Queue与Exchange指定BindingKey时可以使用通配符:
案例:利用SpringAMQP演示TopicExchange的使用
1、声明队列topic.queue1和topic.queue2
2、声明交换机hmall.topic,将两个队列与其绑定
3、编写两个消费者方法,分别监听tpoic.queue1和topic.queue2
4、利用不同的Routingkey向hmall.topic发送消息
生产者
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testSendTopic() {
String exchangeName = "hmall.topic";
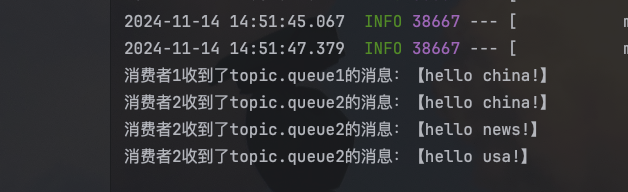
String msg1 = "hello china!";
String msg2 = "hello news!";
String msg3 = "hello usa!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.news", msg1);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "s.news", msg2);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "usa.news", msg3);
}
}消费者
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue1")
public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1收到了topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue2")
public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2收到了topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}
六、声明队列交换机
SpringAMQP提供了几个类,用来声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系:
- Queue:用于声明队列,可以用工厂类QueueBuilder构建
- Exchange :用于声明交换机,可以用工厂类ExchangeBuilder构建
- Binding:用于声明队列和交换机的绑定关系,可以用工厂类BindingBuilder构建
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfiguration {
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
// ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange("").build();
return new FanoutExchange("hmall.fanout2");
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue3() {
// QueueBuilder.durable("ff").build();
return new Queue("hmall.fanout3");
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding3(Queue fanoutQueue3, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue3).to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue4() {
return new Queue("hmall.fanout4");
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding4() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue4()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}SpringAMQP还提供了基于@RabbitListener注解来声明队列和交换机的方式
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "blue"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1收到了direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "yellow"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2收到了direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}七、消息转换器
测试利用SpringAMQP发送对象类型的消息
1、声明一个队列,名为object.queue
2、编写单元测试,向队列中直接发送一条消息,消息类型为Map
3、在控制台查看消息
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>启动类里添加(生产者和消费者都需要添加)
@Bean
public MessageConverter jacksonMessageConverter() {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testSendObject() {
Map<Object, Object> msg = new HashMap<>(2);
msg.put("name", "jack");
msg.put("age", 21);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("object.queue", msg);
}
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "object.queue")
public void listenObjectQueue(Map<Object, Object> msg) {
System.out.println("消费者收到了object.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
// 消费者收到了object.queue的消息:【{name=jack, age=21}】
}
}第二章 高级
2.1 生产者可靠性
一、生产者重连
由于网络波动,可能会出现客户端连接MQ失败的情况。通过配置我们可以开启连接失败后的重连机制
spring:
rabbitmq:
connection-timeout: 1s # 设置MQ的连接超时时间
template:
retry:
enabled: true # 开启超时重试机制
initial-interval: 1000ms # 失败后的初始等待时间
multiplier: 1 # 失败后下次的等待时长倍数, 下次等待时长 = initial - interval * multiplier
max-attempts: 3 # 最大重试次数SpringAMQP提供的重试机制是阻塞式的重试,多次重试等待的过程中,当前线程是被阻塞的,会影响业务性能
如果对业务性能有要求,建议禁用重试机制,可以考虑使用异步线程来执行发送消息的代码
二、生产者确认
RabbitMQ有Publisher Confirm和Publisher Return两种确认机制。开启确认机制后,在MQ成功收到消息后会返回确认消息给生产者,返回结果有以下几种情况
- 消息投递到了MQ,但是路由失败,此时会通过PublisherReturn返回路由异常原因,然后返回ACK,告知投递成功
- 临时消息投递到了MQ,并且入队成功,返回ACK,告知投递成功
- 持久消息投递到了MQ,并且入队完成持久化,返回ACK,告知投递成功
- 其他情况都会返回NACK,告知投递失败
SpringAMQP实现生产者确认
1、在publisher这个微服务的application.yml中添加配置
spring:
rabbitmq:
publisher-confirm-type: correlated # 开启publisher confirm机制,并设置confirm类型
publisher-returns: true # 开启publisher return机制这里publisher-confirm-type有三种模式
- none:关闭confirm机制
- simple:同步阻塞等待MQ的回执消息
- correlated:MQ异步回调方式返回回执消息
2、每个RabbitTemplate只能配置一个ReturnCallback,因此需要在项目启动过程中配置
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class CommonConfig implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
// 获取RabbitTemplate
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RabbitTemplate.class);
// 设置ReturnCallback
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback((message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) -> {
log.info("消息发送失败, 应答码{}, 原因{}, 交换机{}, 路由键{}, 消息{}",
replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey, message.toString());
});
}
}3、发送消息,指定消息ID,消息ConfirmCallback
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ReturnedMessage;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class MqConfirmConfig implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = applicationContext.getBean(RabbitTemplate.class);
// 配置回调
rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback(new RabbitTemplate.ReturnsCallback() {
@Override
public void returnedMessage(ReturnedMessage returnedMessage) {
log.debug("收到消息的return callback, exchange:{}, key:{}, msg:{}, code:{}, text:{}"
, returnedMessage.getExchange(), returnedMessage.getRoutingKey(), returnedMessage.getMessage()
, returnedMessage.getReplyCode(), returnedMessage.getReplyText());
}
});
}
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testConfirmCallback() throws InterruptedException {
// 1.创建cd
CorrelationData cd = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
// 2.添加ConfirmCallback
cd.getFuture().addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<CorrelationData.Confirm>() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
log.debug("消息回调失败", ex);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(CorrelationData.Confirm result) {
log.debug("收到confirm callback回执");
if (result.isAck()){
// 消息发送成功
log.debug("消息发送成功, 收到ack");
} else {
// 消息发送失败
log.error("消息发送失败, 收到nack, 原因:{}", result.getReason());
}
}
});
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hmall.direct", "red", "hello", cd);
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}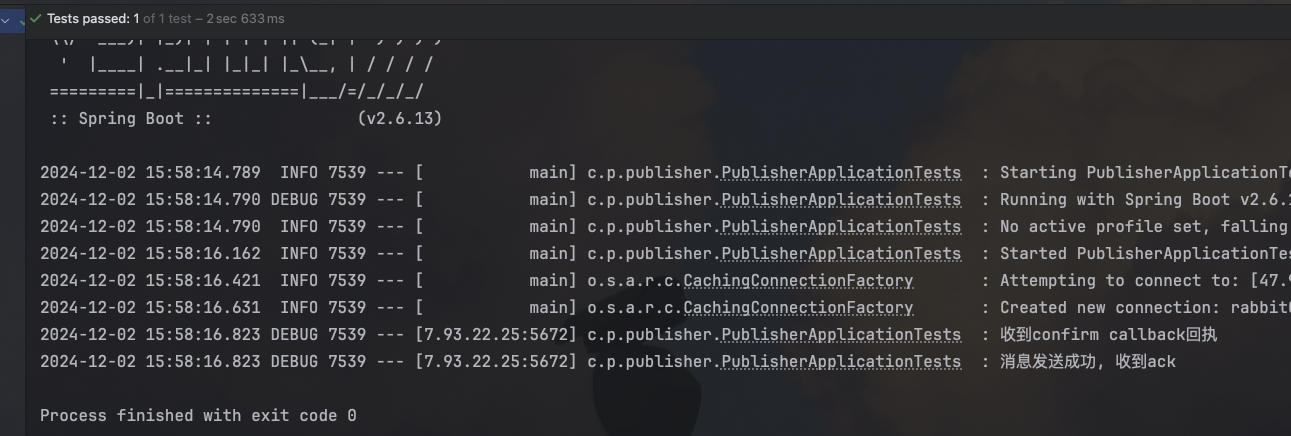
如果key填错
2024-12-02 19:13:21.135 DEBUG 10049 --- [7.93.22.25:5672] c.p.publisher.PublisherApplicationTests : 收到confirm callback回执
2024-12-02 19:13:21.136 DEBUG 10049 --- [7.93.22.25:5672] c.p.publisher.PublisherApplicationTests : 消息发送成功, 收到ack
2024-12-02 19:13:21.131 DEBUG 10049 --- [nectionFactory1] c.priv.publisher.config.MqConfirmConfig : 收到消息的return callback, exchange:hmall.direct, key:red2, msg:(Body:'"hello"' MessageProperties [headers={spring_returned_message_correlation=52b996de-9ffc-4bd1-acbd-04bef206b22b, __TypeId__=java.lang.String}, contentType=application/json, contentEncoding=UTF-8, contentLength=0, receivedDeliveryMode=PERSISTENT, priority=0, deliveryTag=0]), code:312, text:NO_ROUTE如果交换机填错
2024-12-02 19:18:40.675 DEBUG 10094 --- [nectionFactory1] c.p.publisher.PublisherApplicationTests : 收到confirm callback回执
2024-12-02 19:18:40.676 ERROR 10094 --- [nectionFactory1] c.p.publisher.PublisherApplicationTests : 消息发送失败, 收到nack, 原因:channel error; protocol method: #method<channel.close>(reply-code=404, reply-text=NOT_FOUND - no exchange 'hmall.direct123' in vhost '/hmall', class-id=60, method-id=40)2.2 MQ的可靠性
在默认情况下,RabbitMQ会将接收到的信息保存在内存中以降低消息收发的延迟
- 一旦MQ宕机,内存中的消息会丢失
- 内存空间有限,当消费者故障或处理过慢时,会导致消息积压,引发MQ阻塞
一、数据持久化
- 交换机持久化
- 队列持久化
- 消息持久化
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageDeliveryMode;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testPageOut() {
Message message = MessageBuilder.withBody("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
.setDeliveryMode(MessageDeliveryMode.PERSISTENT).build();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.queue", message);
}
}
}PERSISTENT持久的消息
二、Lazy Queue
3.6.0开始,惰性队列,特征:
- 收到消息后直接存入磁盘而非内存(内存中只保留最近的消息,默认2048条)
- 消费者要消费消息时才会从磁盘中读取并加载到内存
- 支持数百万的消息存储
3.12版本后,所有队列都是Lazy Queue模式,无法更改
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(
name = "lazy.queue",
durable = "true",
arguments = @Argument(name = "x-queue-mode", value = "lazy")
))
public void listenLazyQueue(String msg) {
log.info("接收到 lazy.queue的消息:{}", msg);
}
}2.3 消费者的可靠性
一、消费者确认机制
RabbitMQ提供了消费者确认机制(Consumer Acknowledgement),当消费者处理消息结束后,应该向RabbitMQ发送一个回执,告知RabbitMQ自己消息处理状态。回执有三种可选值:
- ack:成功处理消息,RabbitMQ从队列中删除改消息
- nack:消息处理失败,RabbitMQ需要再次投递消息
- reject:消息处理失败并拒绝改消息,RabbitMQ从队列中删除改消息
SpringAMQP已经实现了消息确认功能。并允许我们通过配置文件选择ACK处理方式,有三种方式
none:不处理。即消息投递给消费者后立刻ack,消息会立刻从MQ删除。非常不安全,不建议使用
manual:手动模式。需要自己在业务代码中调用api,发送ack或reject,存在业务入侵,但更灵活
auto:自动模式。SpringAMQP利用AOP对我们的消息处理逻辑做了环绕增强,当业务正常执行时则自动返回ack
当业务出现异常时,根据异常判断返回不同结果:
- 如果是业务异常,会自动返回nack
- 如果是消息处理或校验异常,自动返回reject
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1
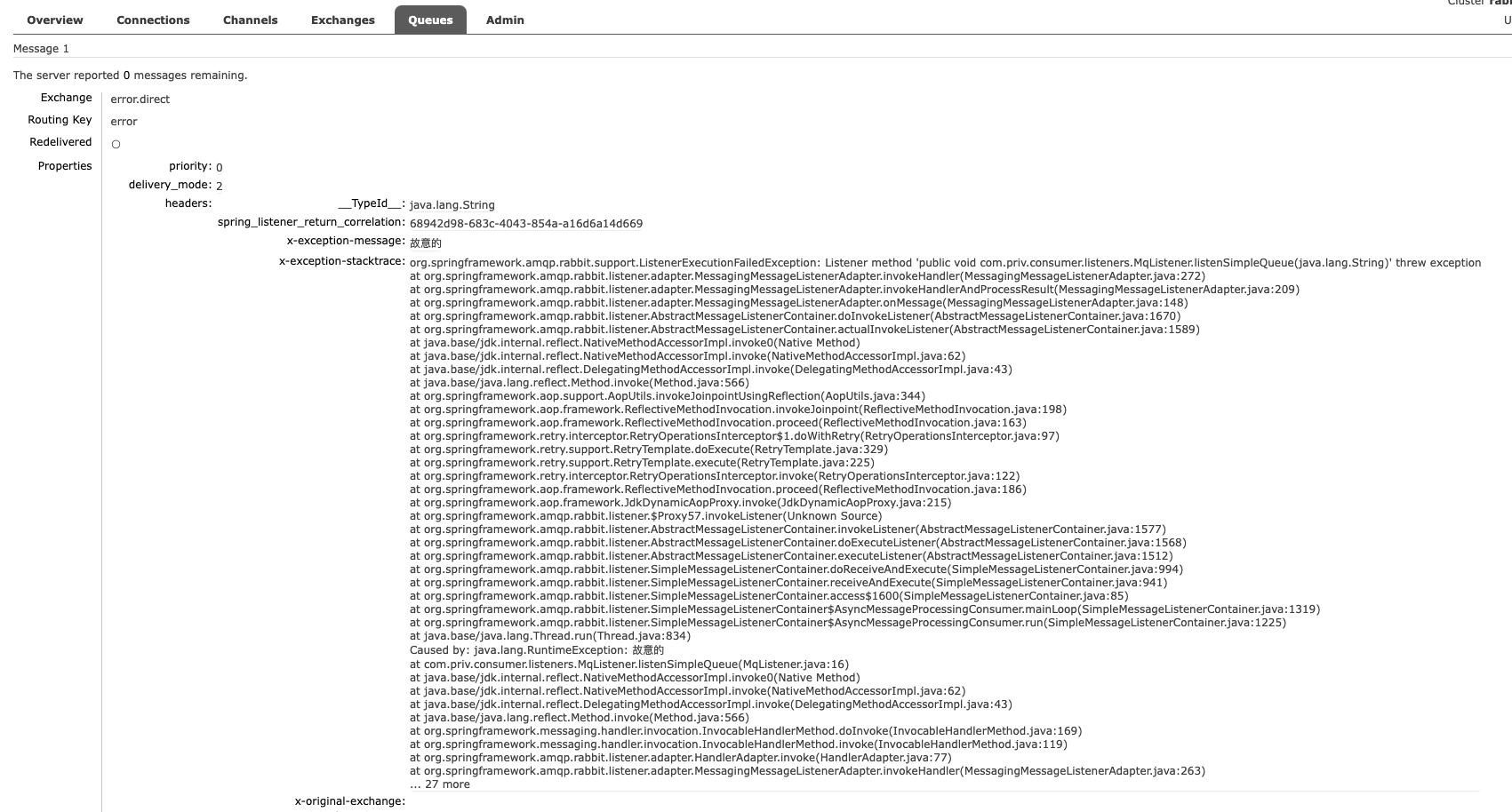
acknowledge-mode: auto # 确认机制 none, 关闭ack; manual, 手动ack; auto, 自动ack二、消费失败处理
当消费者出现异常后,消息会不断requeue(重新入队)到队列,再重新发送给消费者,然后再次异常,再次requeue,无限循环,导致mq的消息处理飙升,带来不必要的压力
我们可以利用Spring的retry机制,在消费者出现异常时利用本地重试,而不是无限制的requeue到mq队列
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息, 处理完成才能获取下一个消息
acknowledge-mode: auto # 确认机制
retry:
enabled: true # 开启消费者失败重试
initial-interval: 1000ms # 初始的失败等待时长为1s
multiplier: 1 # 下次失败的等待时长倍数,下次等待时长 = multiplier * last-interval
max-attempts: 3 # 最大重试次数
stateless: true # true 无状态; false 有状态。 如果业务中包含事务, 这里改为false在开启重试模式后,重试次数耗尽,如果消息依然失败,则需要有MessageRecoverer接口来处理,它包含三种不同的实现:
- RejectAndDontRequeueRecoverer:重试耗尽后,直接reject,丢弃消息,默认就是这种方式
- ImmediateRequeueMessageRecoverer:重试耗尽后,返回nack,消息重新入队
- RepublishMessageRecoverer:重试耗尽后,将失败消息投递到指定的交换机
将失败处理策略改为RepublishMessageRecoverer:
1、定义接收失败消息的交换机、队列及其绑定关系
2、定义RepublishMessageRecoverer
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.retry.MessageRecoverer;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.retry.RepublishMessageRecoverer;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.rabbitmq.listener.simple.retry", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true") // 生效条件
public class ErrorConfiguration {
@Bean
public DirectExchange errorExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("error.direct");
}
@Bean
public Queue errorQueue() {
return new Queue("error.queue");
}
@Bean
public Binding errorBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(errorQueue()).to(errorExchange()).with("error");
}
@Bean
public MessageRecoverer messageRecoverer(RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate) {
return new RepublishMessageRecoverer(rabbitTemplate, "error.direct", "error");
}
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class MqListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueue(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者收到了simple.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
throw new RuntimeException("故意的");
}
}import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageDeliveryMode;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class PublisherApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void testSendMessage2Queue() {
String queueName = "simple.queue";
String msg = "hello amqp";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, msg);
}
}
三、业务幂等性
幂等是一个数学概念,用函数表达式来描述是这样的: f(x) = f(f(x))。在程序开发中,则是指同一个业务,执行一次或多次对业务状态的影响是一致的
幂等:
- 查询业务:例如根据id查询商品
- 删除业务:例如根据id删除商品
非幂等:
- 用户下单业务,需要扣减库存
- 用户退款业务,需要恢复余额
唯一消息id
方案一,是给每个消息都设置一个唯一id,利用id区分是否是重复消息:
- 每一条消息都生成一个唯一的id,与消息一起投递给消费者
- 消费者接收到消息后处理自己的业务,业务处理成功后将消息ID保存到数据库
- 如果下次又收到相同消息,去数据库查询判断是否存在,存在则为重复消息放弃处理
@Bean // 生产者和消费者都要改
public MessageConverter jacksonMessageConverter() {
Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jsonMessageConverter = new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
jsonMessageConverter.setCreateMessageIds(true);
return jsonMessageConverter;
}源码
public final Message toMessage(Object object, @Nullable MessageProperties messagePropertiesArg, @Nullable Type genericType) throws MessageConversionException {
MessageProperties messageProperties = messagePropertiesArg;
if (messagePropertiesArg == null) {
messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
}
Message message = this.createMessage(object, messageProperties, genericType);
messageProperties = message.getMessageProperties();
if (this.createMessageIds && messageProperties.getMessageId() == null) {
messageProperties.setMessageId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
}
return message;
}业务判断
方案二,是结合业务逻辑,基于业务本身做判断。我们要在支付后修改订单状态为已支付,应该在修改订单状态前先查询订单状态,判断状态是否是已支付,只有未支付的订单才需要修改,其他状态不做处理
保证支付服务与交易服务之间的订单状态一致性:
- 支付服务会在用户支付成功以后利用MQ消息通知交易服务,完成订单状态同步
- 为了保证MQ消息的可靠性,采用生产者确认机制、消费者确认机制、消费者失败重试等策略,确保消息投递和处理的可靠性,同时开启MQ的持久化,避免因服务宕机导致消息丢失
- 在交易服务更新订单状态时做了业务幂等判断,避免因消息重复消费导致订单状态异常
如果交易服务消息处理失败,有什么兜底方案?
- 可以在交易服务设置定时任务,定期查询订单支付状态,这样即便MQ通知失败,还可以利用定时任务作为兜底方案,确保订单支付状态的最终一致性
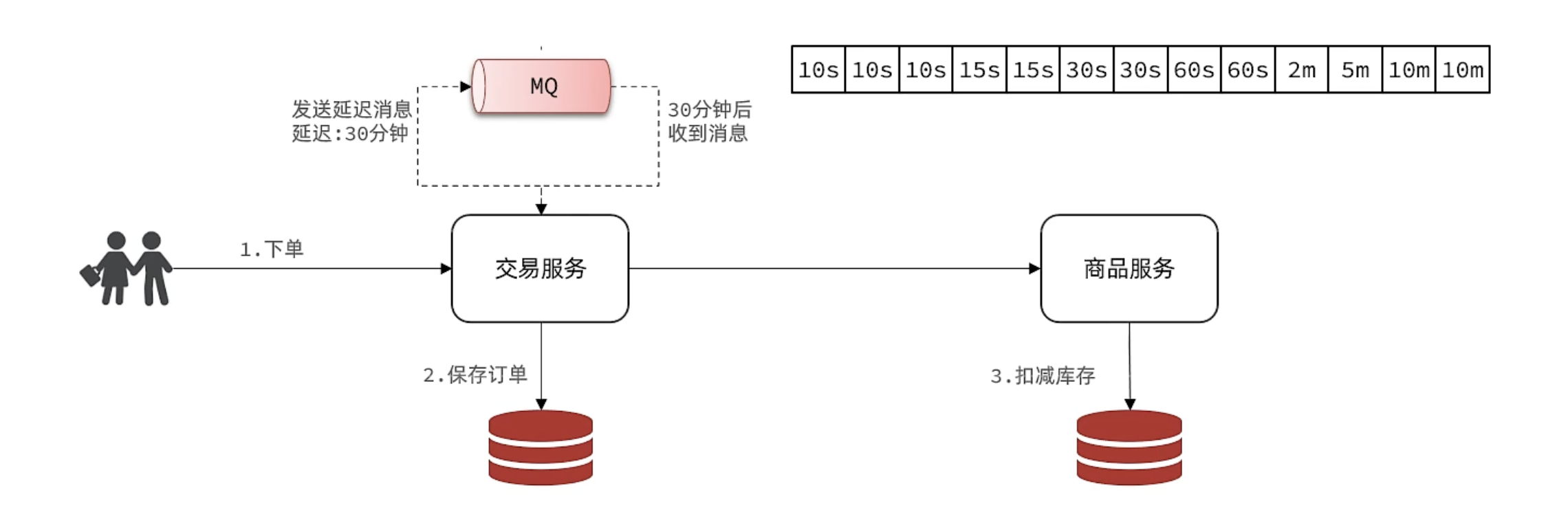
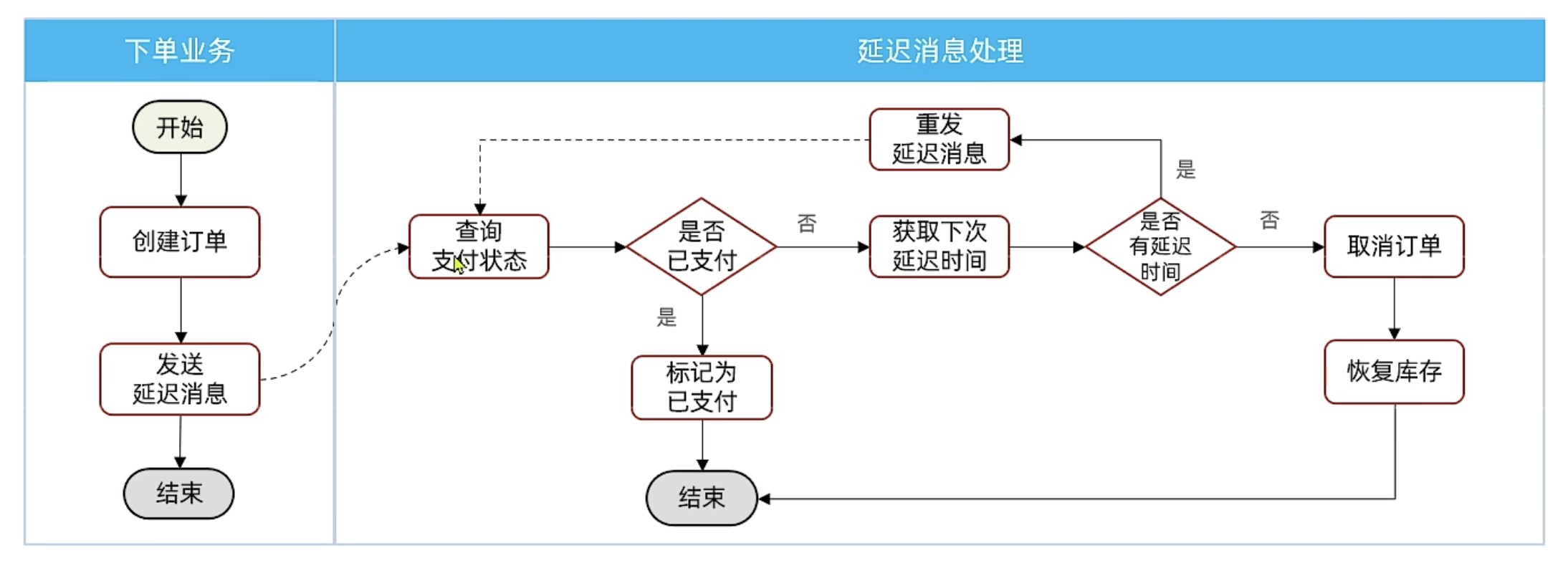
2.4 延迟消息
延迟消息:生产者发送消息时指定一个时间,消费者不会立刻收到消息,而是在指定时间之后才收到消息
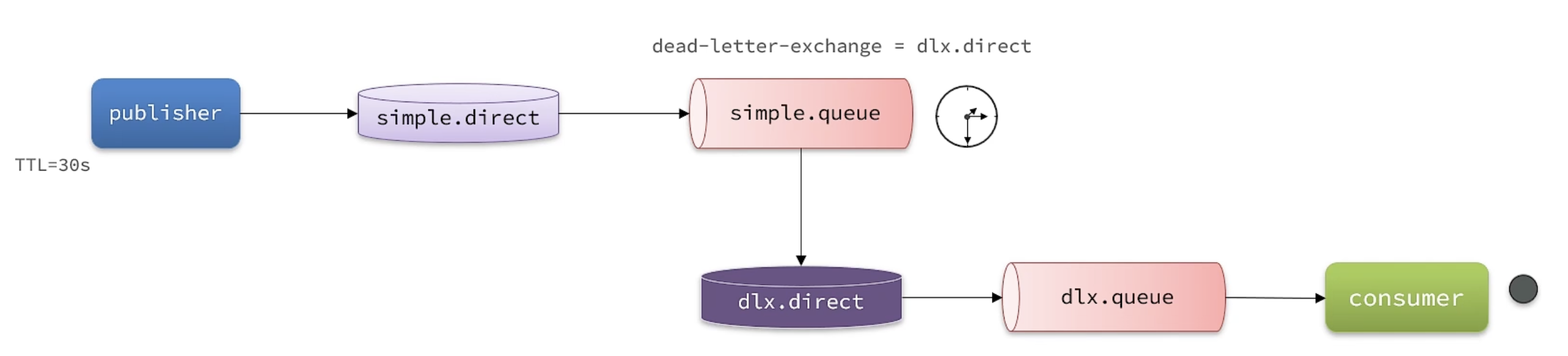
一、死信交换机
当一个队列中的消息满足下列情况之一时,就会成为死信(dead letter)
- 消费者使用basic.reject或basic.nack声明消费失败,并且消息的requeue参数设置为false
- 消息是一个过期消息(达到了队列或消息本身设置的过期时间),超时无人消费
- 要投递的队列消息堆积满了,最早的消息可能成为死信
如果队列通过dead-letter-exchange属性指定了一个交换机,那么该队列中的死信就会投递到这个交换机中,这个交换机称为死信交换机(Dead Letter Exchange,简称DLX)
二、延迟消息插件


三、取消超时订单
设置30分钟后检测订单支付状态,存在的问题:
- 如果并发较高,30分钟可能堆积消息过多,对MQ压力很大
- 大多数订单在下单后1分钟内就会支付,但是却需要在MQ内等待30分钟,浪费资源