SpringBoot——运维篇
第一章 运维
1.1打包与运行
Windows
一、对SpringBoot项目打包
mvn package二、运行项目
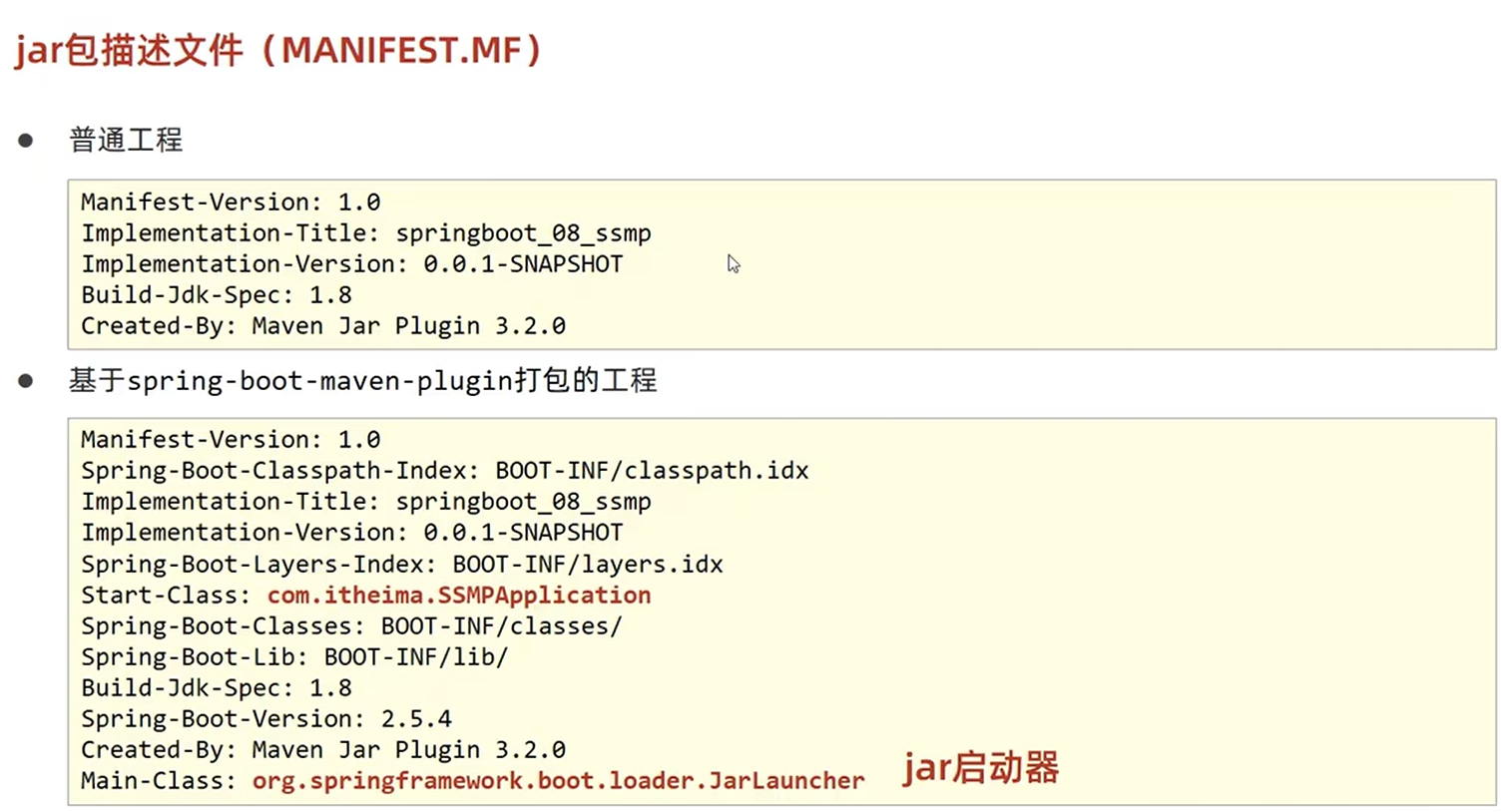
java -jar springboot.jar问题:遇到jar中没有主清单属性
打包插件
- 使用SpringBoot提供的maven插件可以将工程打包成可执行jar包
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>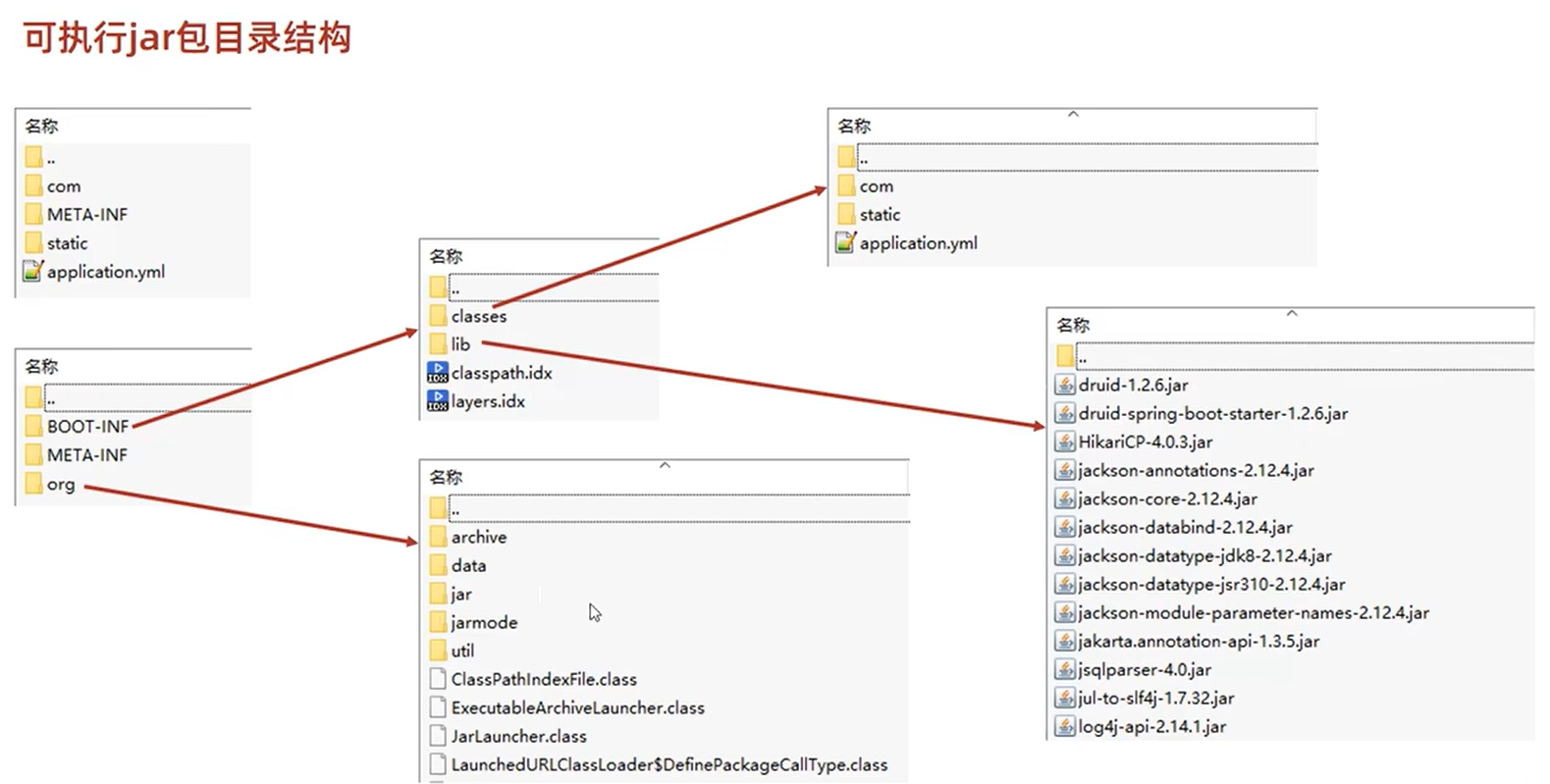
- Windows端口被占用
#查询端口
netstat -ano
#查询指定端口
netstat -ano |findstr "端口号"
#根据进程PID查询进程名称
tasklist |findstr "进程PID号"
#根据PID杀死任务
taskkill /F /PID "进程PID号"
#根据进程名称杀死任务
taskkill -f -t -im "进程名称"Linux
安装JDK,版本不低于打包使用的JDK版本
安装包保存在/user/local/自定义目录中或$HOME下
其他按照windows版本进行
1.2配置高级
临时属性设置
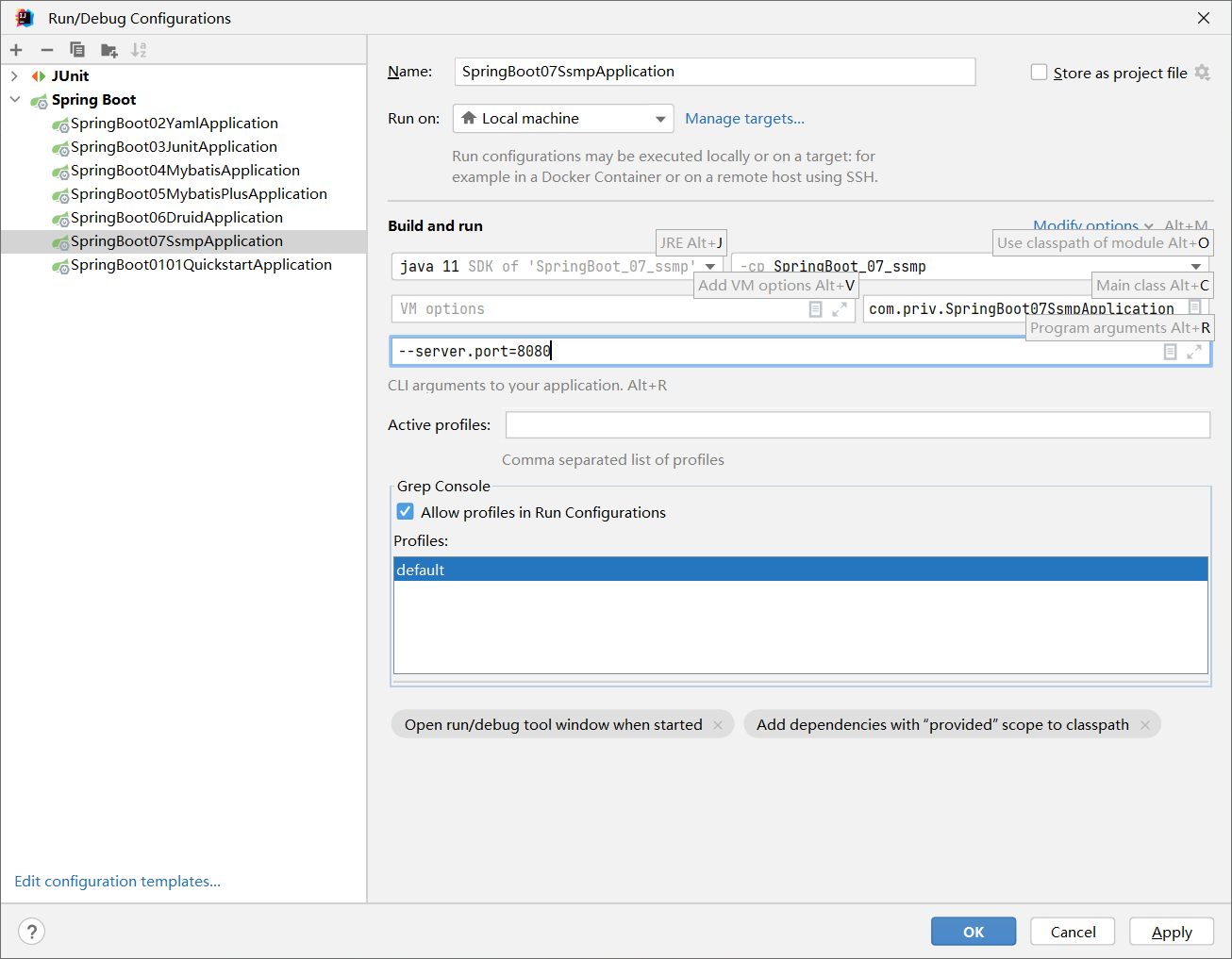
带属性数启动SpringBoot
java -jar springboot.jar --server.port=8080携带多个属性启动SpringBoot,属性间使用空格分隔
- 带属性启动SpringBoot程序,为程序添加运行属性
- 通过编程
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] arg = new String[1];
arg[0] = "--server.port=8080";
SpringApplication.run(SSMPAplication.class, arg);
//设置不传数组参数(例如上面的arg),可以保障程序的安全性,即后期不能携带临时属性
}配置文件分类
一、SpringBoot中4级配置文件
1级:file:config/application.yml 【最高】
2级:file:application.yml
3级:classpath:config/application.yml
4级:classpath:application.yml 【最低】
二、作用
1级与2级留做系统打包后设置通用属性,1级常用于运维经理进行线上整体项目部署方案调控
3级与4级用于系统开发阶段设置通用属性,3级常用于项目经理进行整体项目属性调控
自定义配置文件
- 通过启动参数加载配置文件
- 通过启动参数加载指定文件路径下的配置文件
--spring.config.location=classpath:/ebank.properties
--spring.config.location=classpath:/ebank.properties,classpath:/ebank-server.properties
#最后一个生效,相同覆盖,不同生效重要说明
- 单服务器项目:使用自定义配置文件需求较低
- 多服务器项目:使用自定义配置文件需求较高,将所有配置放置在一个目录中,统一管理
- 基于SpringCloud技术,所有的服务器将不再设置配置文件,而是通过配置中心进行设置,动态加载配置信息
1.3多环境开发
YAML版
#应用环境
#公共配置
spring:
profiles:
active: pro
---
#设置环境
#生产环境
spring:
profiles: pro
server:
port: 8080
---
#开发环境
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 8081
---
#测试环境
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: test
server:
port: 8082多文件版
application.yml
#应用环境
#公共配置
spring:
profiles:
active: proapplication-dev.yml
server:
port: 8080application-pro.yml
server:
port: 8081application-test.yaml
server:
port: 8082Properties版
如上,书写格式写成properties版即可
书写技巧
include属性
拆分:
- application-devDB.yml
- application-devRedis.yml
- application-devMVC.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
include: devDB,devRedies,devMVCtips:当主环境dev与其他环境有相同属性时,主环境属性生效;其他环境中有相同属性时,最后加载的环境属性生效。
group属性
从SpringBoot2.4版开始使用group属性替代include属性。
group属性定义多种主环境与子环境的包含关系
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
group:
"dev": devDB,devRedis,devMVC
"pro": proDB,proRedis,proMVC
"test": testDB,testRedis,testMVC多环境开发控制
1、Maven中设置多环境属性
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev_evn</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>pro_evn</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>pro</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>test_evn</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>test</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>2、SpringBoot中引用Maven属性
spring:
profile:
active: @profile.active@3、执行Maven打包指令,并在生成的boot打包文件.jar文件中查看对应信息
基于SpringBoot读取Maven配置属性的前提下,如果在Idea下测试工程时pom.xml每次更新需要手动compile方可生效
1.4日志
日志基础
log的作用
- 编程期调试代码
- 运营期记录信息
- 记录日常运营重要信息(峰值流量、平均响应时长…)
- 记录应用报错信息(错误堆栈)
- 记录运维过程数据(扩容、宕机、报警…)
代码实现
只会显示等级大于等于当前level的信息
设置日志输出级别:
server:
port: 8080
#开启debug模式,输出调试信息,常用于检查系统运行状况
debug: true
#设置日志级别,root表示根节点,即整体应用日志级别
logging:
#设置分组
group:
ebank: com.priv.controller,com.priv.service,com.priv.dao
level:
root: debug
#设置某个包的日志级别
#com.priv.controller: debug
#设置分组,对某个组设置日志级别
ebank: warnpackage com.priv.controller;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author : 十一
* @data : 09:02 2023/2/22
* When in doubt, use brute force.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
/**
* 创建记录对象的日志
*/
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BookController.class);
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("springboot is running...");
log.debug("debug...");
log.info("info...");
log.warn("warn...");
log.error("error...");
return "springboot is running...";
}
}日志级别
- TRACE:运行堆栈信息,使用率低
- DEBUG:程序员调试代码使用
- INFO:记录运维过程数据
- WARN:记录运维过程报警数据
- ERROR:记录错误堆栈信息
- FATAL:灾难信息,合并计入ERROR
使用lombok提供的@Slf4j注解简化开发
package com.priv.controller;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author : 十一
* @data : 09:02 2023/2/22
* When in doubt, use brute force.
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController extends BaseClass{
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("springboot is running...");
log.debug("debug...");
log.info("info...");
log.warn("warn...");
log.error("error...");
return "springboot is running...";
}
}日志输出格式配置

- PID:进程ID,用于表明当前操作所处的进程,当多服务同时记录日志时,该值可用于协助程序员调试程序
- 所属类/接口名:当前显示信息为SpingBoot重写后的信息,名称过长时,简化包名书写为首字母,甚至直接删除
设置日志输出格式
logging:
pattern:
console: "%d - %m%n"- %d:日期
- %m:消息
- %n:换行
logging:
pattern:
console: "%d %clr(%p) --- [%16t] %clr(%-40.40c){cyan} : %m %n"日志文件
设置日志文件
logging:
file:
name: server.log日志文件详细配置
logging:
file:
name: server.log
logback:
rollingpolicy:
max-file-size: 3kB
file-name-pattern: server.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log小结
SpringBoot运维部分完结,代码请查看GitHub仓库